Go, originating from China with a history spanning over 2500 years, and chess, originating from India and dating back approximately 1500 years, are the most popular strategic board games in the world. Significant not only in terms of entertainment but also culturally. The rules are clear and precise, making the entry threshold for new players for both of these games very low. It is this simplicity that gives rise to the invention of original solutions. It also about tactics and, above all, enormous human intellectual effort. All that to defeat the opponent.
Artificial Intelligence is not only the subject of serious applications such as Intelligent Acoustics in industry, Artificial Intelligence Adaptation in development research or Data Engineering. These and other algorithms are also used in various fields of entertainment. They are used to create models, artificial players to beat human players in board games and even in e-sports.
At the turn of the 20th and 21st centuries, chess and Go lived to see their digital versions. Computer games also emerged, with players vying for first place on the board and e-sports titles. In parallel with these, several artificial intelligence models with appropriately implemented rules have emerged to search for better plays and beat human players. In this post, I am going to describe how board games, computer games and artificial intelligence complement and inspire each other. I am also going to show how a properly trained artificial intelligence model has defeated not only individual modern grandmasters, but also entire teams.
Artificial intelligence conquers board games
How artificial intelligence defeated a chess grandmaster has its roots in the Deep Blue project led by IBM. The main goal of the project was to create a computerised chess system. Deep Blue was the result of years of work by scientists and engineers. The first version of Deep Blue was developed in the 1980s. It used advanced algorithms, i.e.:
- Tree Search based on a database of chess moves and positions,
- Position Evaluation,
- Depth Search.
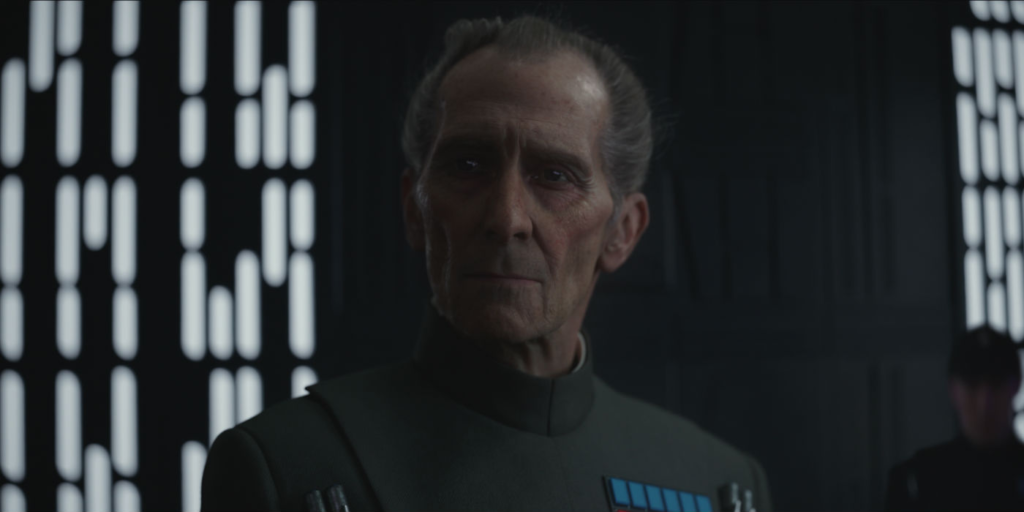
In 1996, the first match between Deep Blue and Garri Kasparov took place. This match was experimental and was the first official meeting of its kind. Kasparov won three games, drawing and losing one. In May 1997, they clashed again in New York. This time, Garii Kasparov fell in a duel with artificial intelligence. Deep Blue won twice and lost only once. A draw was declared three times.

Fig. 1 Garii Kasparov during a game against Deep Blue in May 1997.
Less is more
An equally interesting case is a programme created by DeepMind called AlphaGo. This artificial intelligence was designed to play Go, as the world found out when it beat Go grandmaster Lee Sedol. Go is much more difficult than other games, including chess. This is due to the much larger number of possible moves. It makes it difficult to use traditional AI methods such as exhaustive search [1, 2]. DeepMind started work on the AlphaGo programme in 2014. The aim was to create an algorithm that could compete with the masters. It used advanced machine learning techniques:
- Deep Learning,
- Reinforcement Learning (RL),
- Monte Carlo Tree Search.
AlphaGo’s first significant achievement was beating European competitor Fan Hui in October 2015. The engine from DeepMind completely dominated each game, thus winning five to zero [3]. The next step was to defeat grandmaster Lee Sedol. During the matches, artificial intelligence surprised not only its opponent but also experts with its unconventional and creative moves. The programme demonstrated its ability to anticipate strategies and adapt to changing conditions on the board. As a result, after games played from 9-15 March 2016, AlphaGo claimed a historic victory over Lee Sedol, winning the five-match series 4-1.
Competition on digital boards
In 2018, OpenAI created a team of artificial players, the so-called bots, dubbed the OpenAI Five. The bot team faced professional players in Dota 2, one of the most complex MOBA (Multiplayer Online Battle Arena) games. Two teams of five players battle against each other to destroy the opponent’s base. Several advanced machine learning techniques and concepts were used to ‘train’ OpenAI Five:
- Reinforcement Learning – bots learned to make decisions by interacting with the environment and receiving rewards for certain actions,
- Proximal Policy Optimisation (PPO) – this is a specific RL technique that, according to the developers, was crucial to its success [5]. This method optimises the so-called policy (i.e. decision-making strategy) in a way that is more stable and less prone to oscillations compared to earlier methods such as Trust Region Policy Optimisation (TRPO) [6].
- Spontaneous learning – artificial players played millions of games against each other. This allowed them to develop increasingly sophisticated strategies, learning from their mistakes and successes.
In August 2018, artificial intelligence beat the semi-professional Pain Gaming team at the annual world championship ‘The International’. In 2019, at the OpenAI Five Finals event, the bots defeated a team made up of top players. It included members of the OG team, winners of The International in 2018. DeepMind, on the other hand, decided not to stop with AlphaGo and turned its focus towards StarCraft II, one of the most popular real-time strategy (RTS) games, by creating the AlphaStar programme. AI went into one-on-one duels with professional StarCraft II players in 2019. In January, it defeated the strategy’s top players — Gregory “MaNa” Komincz twice — and also won over Dario “TLO” Wünsch. AlphaStar thus proved its capabilities.
Artificial Intelligence in e-sports
Artificial intelligence is playing an increasingly important role in the training of professional e-sports teams. Especially in countries such as South Korea, where the League of Legends is one of the most popular games. Here are some key areas where AI is being used for training in professional organisations such as T1, and Gen.G.
Analytics teams use huge amounts of collected data from league and friendly matches. They analyse match statistics such as number of assists, gold won, most frequently taken paths and other key indicators. This allows coaches to identify patterns and weaknesses in both their players and opponents.
Advanced training tools using artificial intelligence, such as ‘AIM Lab’ or ‘KovaaK’s’, help players develop specific skills. Such tools can personalise training programmes that focus on improving reactions, aiming, tactical decisions and other key aspects of the game.
They are also used to create advanced simulations and game scenarios while mimicking various situations that may occur during a match. This allows players to train under conditions closely resembling real-life scenarios. This allows players to better prepare for unexpected events and make better decisions faster during actual matches.
AI algorithms can be used to optimise team composition by analysing data on individual player skills and preferences. The results of such studies can suggest which players should play in which positions. They can also help select line-ups to maximise team effectiveness.
Conclusions
This article shows how artificial intelligence has dominated board games and made a permanent presence in e-sports. It has defeated human champions in chess, Go, Dota 2 and StarCraft II. The successes of projects such as Deep Blue, AlphaGo, OpenAI Five and AlphaStar show the potential of AI in creating advanced strategies and improving gaming techniques. Future development opportunities include its use in creating more realistic scenarios, developing detailed and personalised player development paths, and predictive analytics that can revolutionise training and strategy across industries.
References
[1] Google achieves AI ‘breakthrough’ by beating Go champion, “BBC News”, 27 January 2016
[2] AlphaGo: Mastering the ancient game of Go with Machine Learning, “Research Blog”
[3] David Larousserie et Morgane Tual, Première défaite d’un professionnel du go contre une intelligence artificielle, “Le Monde.fr”, 27 January 2016, ISSN 1950-6244
[4] https://openai.com/index/openai-five-defeats-dota-2-world-champions/ accessed 13 June 2024
[5] https://openai.com/index/openai-five/ accessed 13 June 2024
[6] Schulman, J., Wolski, F., Dhariwal, P., Radford, A., & Klimov, O. (2017). Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.06347.